Curriculum planning Edit for timeliness • Review the maps for timely issues, breakthroughs, methods, materials, and new types of assessment • Be vigilant about technology Edit for Coherence • Scrutinize maps for a solid match between the choice of content, the featured skills and· Curriculum development the Philippine experience Adelaida Bago LB 3 01 · Curriculum development theory into practice Daniel Tanner LB 1870 T352 1980 · Curriculum planning for better school Gaudencio Aquino LB 1570 A68 1986 · An Early childhood curriculum for developmental model to application Eva EssaCurriculum Development The Philippine Experience reviews policies and practices in the development, implementation and evaluation of curricula in the country from the preSpanish period to contemporary times The book relates past and present policies and practices in basic and secondary education to theories, principles and other technical
Understanding By Design Center For Teaching Vanderbilt University
Diagram explaining the goal-based model of curriculum planning in the philippines
Diagram explaining the goal-based model of curriculum planning in the philippines-Outcomebased education is a model of education that rejects the traditional focus on what the school provides to students, in favor of making students demonstrate that they "know and are able to do" whatever the required outcomes areParticipants in Curriculum Development and Planning • Teachers • Students • Principals • Parents • Curriculum Specialists • Superintendents GOALBASED MODEL OF CURRICULUM PLANNING, THE PHILIPPINE EXPERIENCE Outcome Goals of the K to12 Basic Education Program The K to 12 Basic Education Program seeks to realize the following


Like The Layers Of An Onion Curricular Noticing As A Lens To Understand The Epistemological Features Of The Philippine K To 12 Secondary Mathematics Curriculum Materials Springerlink
· Curriculum development the Philippine experience Adelaida Bago LB 3 01 · Curriculum development theory into practice Daniel Tanner LB 1870 T352 1980 · Curriculum planning for better school Gaudencio Aquino LB 1570 A68 1986 · An Early childhood curriculum for developmental model to application Eva EssaOverview The Grid is a model to construct differentiated curriculum It includes and organizes all the various components needed in a differentiated curriculum To begin planning the curriculum, it is necessary to have a theme, rather than a topic as the organizing elements The components of the grid are content, processesUnit describes a variety of models of curriculum design in order to make this complex activity understandable and manageable It is important for you as a teacher to understand how the curriculum you are using in your school was designed Objectives After completing this unit, you should be able to 1 Discuss various models of curriculum
Curriculum evaluation It then describes several evaluation models It concludes by propos ing a comprehensive and eclectic process that can be used to evaluate a field of study, which is perhaps the most difficult curricular element that evaluators face Curriculum Evaluation CHAPTER 12 • • What principles best define curriculumDescribe the goalbased model of curriculum planning in the Philippines using a diagram Compare the curriculum planning models Steps/Elements/Components Identify the participants in Curriculum Development and Planning and discuss their main role Group Report Students presentation of the diagram of the goalbased model of curriculum planning in the Philippines Three most important sectors in Curriculum Planning Decisions Choosing one curriculum model and planning relevant to the 21 st centuryModels of curriculum evaluation have developed over time and have reflected the climate and values of the times they were developed For the purposes of this article, goal based and goal free evaluation will be examined through Ralph Tyler's objective oriented approach and Michael Scriven's goal free evaluative approach
January , 21 DM 001, s 21 – 21 International Day of EducationCurrent curriculum models can be broken down into two broad categories—the product model and the process model The product model is resultsoriented Grades are the prime objective, with the focus lying more on the finished product rather than on the learning process1 Definitions Curriculum planning refers to the creation of a curriculum There is no clear definition of what a curriculum is Some definitions are rather centered around student activities, eg curriculum is the planned engagement of learnersSome are more subject centered, eg "curriculum is the subject matter taught to students or an arrangement of instructional materials


Philippine Professional Standards For Teachers Ppst Teacherph


Details Philippine Qualifications Framework
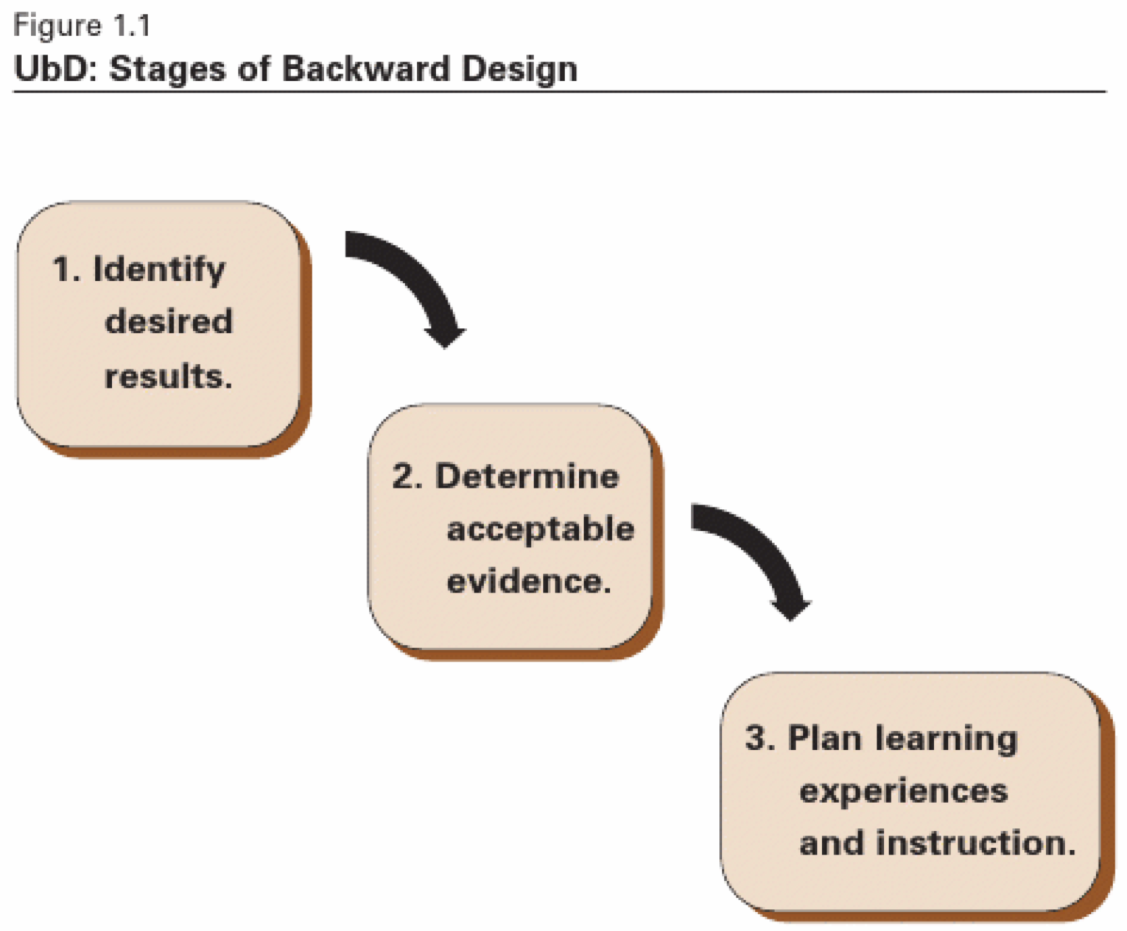
The action planning workbook by Charles Schwahn that follows in this chapter of the ASCD Curriculum Handbook stems from this TOBE approach The McREL Model An approach complementary to OBE that many educators have found to be helpful is the performance assessment system developed by Bob Marzano and associates at the Midcontinent RegionalBackward design challenges "traditional" methods of curriculum planning In traditional curriculum planning, a list of content that will be taught is created and/or selected 4 In backward design, the educator starts with goals, creates or plans out assessments and finally makes lesson plansPlanning the research lesson In Japan, Lesson Study takes place across all curriculum areas, as well as in noncurriculum areas such as class meetings, although it is probably more common in mathematics and science than some other areas In mathematics, the research lesson, at least at the primary school level,



Curriculum Models Ppt Video Online Download



Developing A Curriculum For The Transition Program Of Special Learners In The Philippines Semantic Scholar
Recent DepEd Memoranda February 5, 21 DM 002, s 21 – Ulirang Guro 21 ng Komisyon ng Wikang Filipino;Bureau of Curriculum Development Develops and manages the national education policy framework on curriculum development and management for the Department Develops national curriculum standards for basic education Designs and develops special curriculum programs appropriate for all types of learnersThe action planning workbook by Charles Schwahn that follows in this chapter of the ASCD Curriculum Handbook stems from this TOBE approach The McREL Model An approach complementary to OBE that many educators have found to be helpful is the performance assessment system developed by Bob Marzano and associates at the Midcontinent Regional
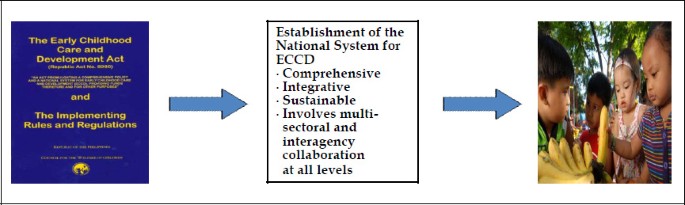


Legal Frameworks For Early Childhood Governance In The Philippines International Journal Of Child Care And Education Policy Full Text
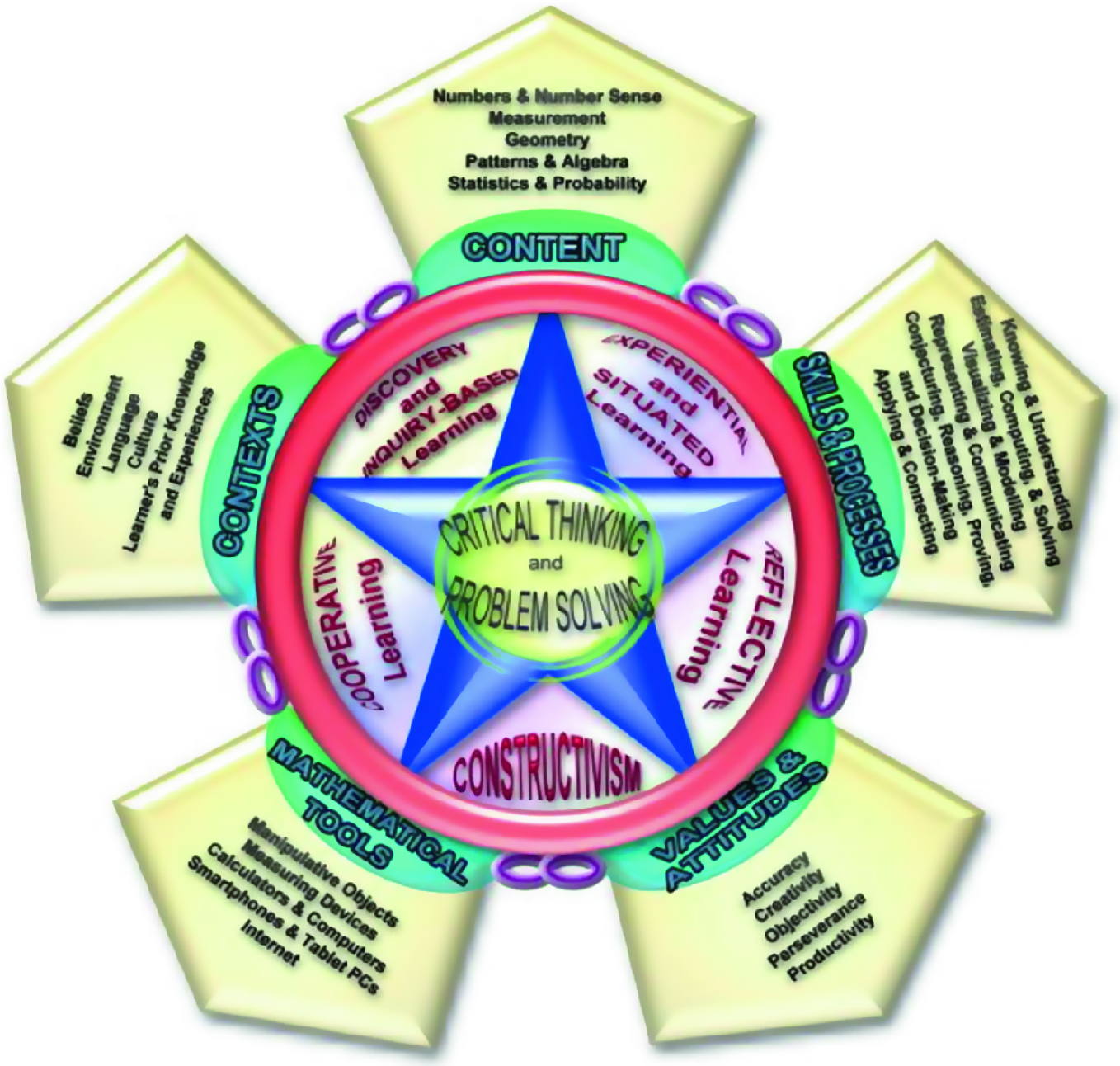


Prospects And Challenges In Implementing A New Mathematics Curriculum In The Philippines Springerlink
Like everything else in the Philippines, planning is not taken seriously We all need to realize that the K to 12 is a catchup attempt to put the Philippines at par with the rest of the world Our curriculum has been criticized as being fraught with rote memorization, and K to 12 is expected to change all thatEducational goals and plan Parents, and other family members, are engaged as meaningful partners in the special education process and the education of their child in the general education curriculum Teachers provide researchbased instructional teaching and learningTherefore, curriculum in the 21st century should focus on the construction of knowledge and encourage students to produce the information that has value or meaning to them in order to develop new skills Preparing curriculum to be connected with the real world can support student participation, their motivation and



Curriculum Planning In The Philippines



High Quality Health Systems In The Sustainable Development Goals Era Time For A Revolution The Lancet Global Health
An alternative, process model of curriculum creation is described and claims are made about the advantages it can have as an approach to planning coherent learning programmes View Show abstractThe desired result of instruction is an important part of curriculum planning and must be determined to successfully plan instruction Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe, coauthors and educators, identified a method of writing curriculum that they refer to as Backward Design Their program suggests that curriculum writers ask themselves threeJanuary , 21 DM 001, s 21 – 21 International Day of Education
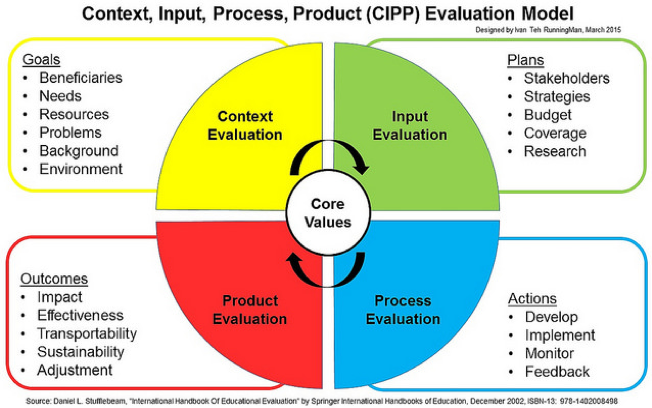


Cipp Model Poorvu Center For Teaching And Learning



Pdf A Curriculum Framework For The Sustainable Development Goals First Edition
The Well Model Should Show 1 major component of the process, including stages of planning, implementation, and evaluation 2 customary but not inflexible "beginning" and "ending" points 3 the relationship between curriculum and instruction 4 distinctions between curriculum and instructional goals and objectivesIt describes the dynamics on how variuos curriculum workers strive to do their functions in order to attain education goals, programs and policies set by the country region, division,distinct and down to the local school level and each levels has specific functions to doCurriculum implementation is influenced by the educational goals set by the government or schools, however, the process of curriculum implementation is also guided by an educational or curriculum philosophyParents as Teachers builds strong communities, thriving families and children that are healthy, safe and ready to learn Our parent educators use an evidencebased home visiting model with parents and caregivers during a child's earliest years in life, from prenatal through kindergarten Our evidenc
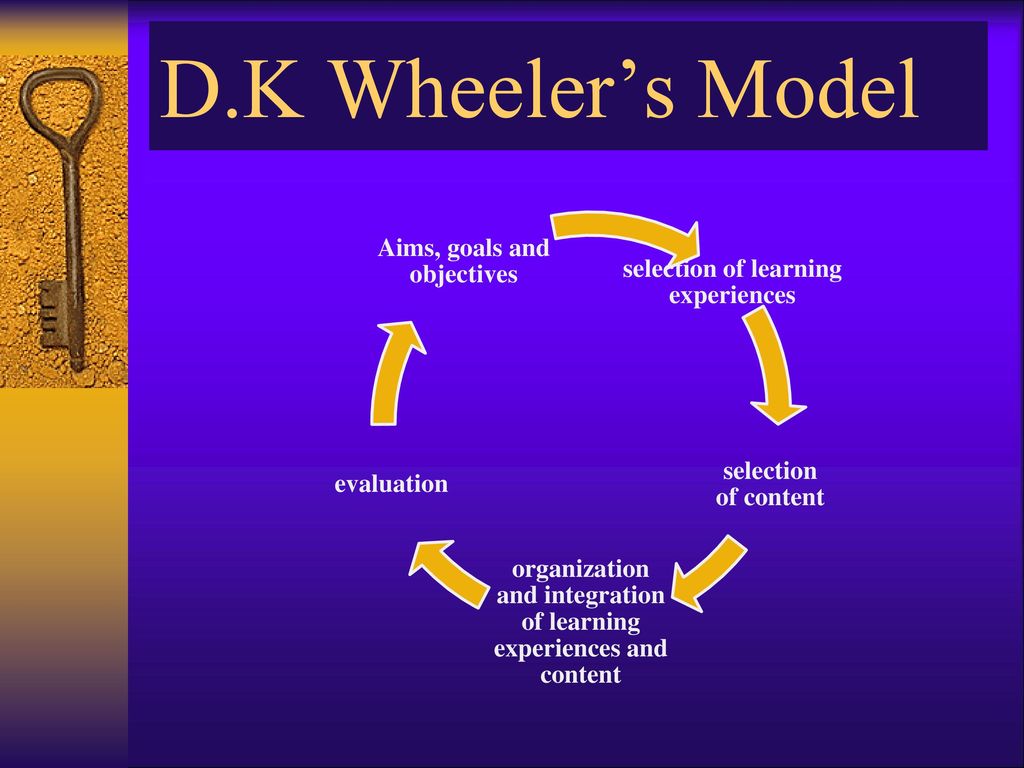


Cyclical Models Of Curriculum Development Ppt Download



Pdf Introduction Of Outcome Based Education In Philippine Health Professions Education Setting 1 2 3
Curriculum planning Edit for timeliness • Review the maps for timely issues, breakthroughs, methods, materials, and new types of assessment • Be vigilant about technology Edit for Coherence • Scrutinize maps for a solid match between the choice of content, the featured skills andTopic#3 Model for Curriculum Development Objectives Students should be able to identify models for curriculum development Students can distinguish objective model from dynamic model in curriculum development 31 Definition Model refers to relationship between the parts of the process of curriculum development, ie objectives,Curriculum planning in the philippines presented by christian d evangelista marianne t evangelista, mshrm divine mercy college foundation inc Caloocan City Slideshare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising



Curriculum Planning In The Philippines



The K To 12 Basic Education Program Official Gazette Of The Republic Of The Philippines
Halliwell's model is particularly interesting because it implies that the curriculum developer need not start with aims A wcakne~s of both models is the implication that all of the outcomes of an educational process are amenable to evaluation (or This is not (al the present moment' in time) true For e"a",ple,Halliwell's model is particularly interesting because it implies that the curriculum developer need not start with aims A wcakne~s of both models is the implication that all of the outcomes of an educational process are amenable to evaluation (or This is not (al the present moment' in time) true For e"a",ple,5 Selection of learning experiences 6 Organization of learning activities 7 Determination of what to evaluate and the means of doing it Thus as you look into curriculum models, the three interacting processes in curriculum development are planning, implementing and evaluating



Goal Based Model Of Curriculum Planning Yam Heam Youtube
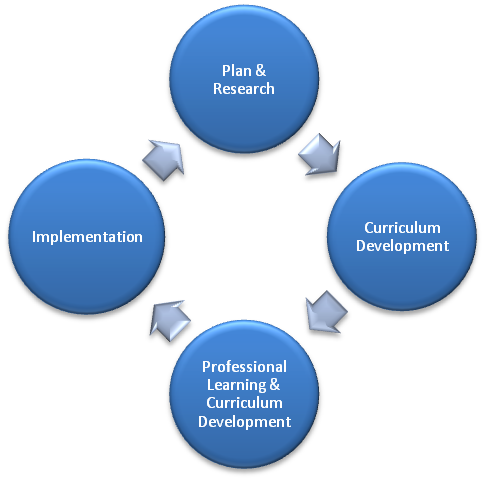


Learning Services Curriculum Development
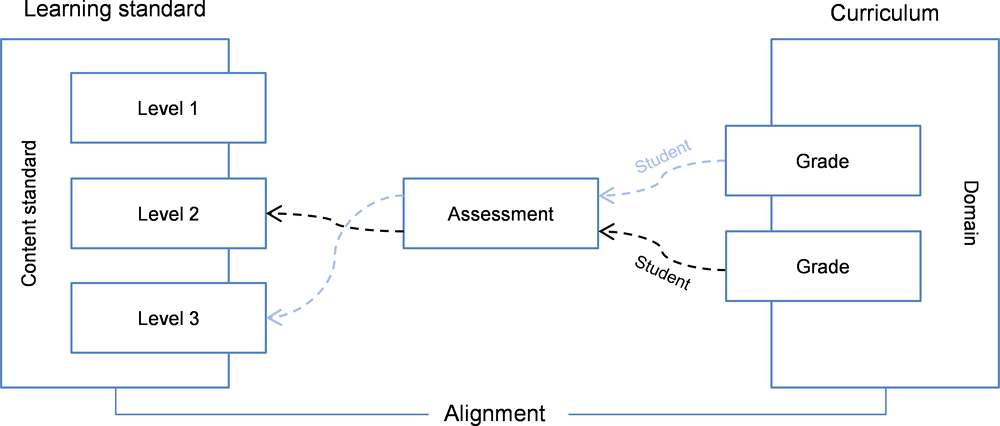
Each performance indicator is assigned to one of six curriculumplanning levels that represent a continuum of instruction ranging from simple to complex The levels can serve as building blocks for curriculum development in that students should know and be able to perform the performance indicators· Curriculum development the Philippine experience Adelaida Bago LB 3 01 · Curriculum development theory into practice Daniel Tanner LB 1870 T352 1980 · Curriculum planning for better school Gaudencio Aquino LB 1570 A68 1986 · An Early childhood curriculum for developmental model to application Eva EssaFar too often, organizations choose the wrong approach to strategic planning As a result, strategic plans sit untouched on shelves and planners become even more cynical about the strategic planning process This occurs especially with 1) new organizations, 2) organizations having many current issues, and 3) organizations having very limited resources



Curriculum Planning In The Philippines



Chapter 5 Curriculum Development And Planning Curriculum Goal
The Tyler Model One of the best known models for curriculum development with special attention to the planning phases is Ralph W Tyler's in his classic little book, Basic Principles of Curriculum and Instruction, "The Tyler Rationale", a process for selecting educational objectives, is widely known and practiced in curriculum circlesPurpose of Curriculum Design Teachers design each curriculum with a specific educational purpose in mind The ultimate goal is to improve student learning, but there are other reasons to employ curriculum design as wellFor example, designing a curriculum for middle school students with both elementary and high school curricula in mind helps to make sure that learning goals are aligned andThe desired result of instruction is an important part of curriculum planning and must be determined to successfully plan instruction Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe, coauthors and educators, identified a method of writing curriculum that they refer to as Backward Design Their program suggests that curriculum writers ask themselves three



Curriculum Planning In The Philippines



Writing Curriculum Aims Goals Objectives
To understand curriculum models we need to take a step back and talk about curriculum itself Curriculum can be defined as a plan used in education that directs teacher instruction"the inhabitants were a civilized people, possessing their system of writing, laws and moral standards in a well organized system of government They did not have an organized system of education as we have now" "the curriculum for boys and girls was aimed to teach them toEvaluation specialists have proposed an array of models 30 Model of curriculum evaluation Tyler's ObjectivesCentered Model One of the earliest curriculum evaluation models, which continue to influence many assessment projects, was that proposed by Ralph Tyler (1950) in his monograph Basic Principles of Curriculum and Instruction



Curriculum Planning Process Development Educational Psychology Class Video Study Com



Chapter 5 Curriculum Development And Planning Curriculum Goal
Implementation of a plan for instruction Regardless of definition or approach, curriculum can be organized into three major components objectives, content or subject matter, and learning experiences Think of objectives as a road map ("where" are we going), content as the "what" of curriculum, and learning experiences as the "how"Becoming a Great High School by Tim R Westerberg Table of Contents Chapter 3 Strategy 1 Developing Clear Instructional Goals Approaching instruction with clear instructional goals, or to borrow a phrase popularized by Stephen Covey, beginning with the end in mind, not only makes intuitive sense but is well supported by researchOliva (09) defines curriculum as A plan or program for all the experiences that the learner encounters under the direction of the school In practice, the curriculum consists of a number of plans, in written form and of varying scope and detail that delineate the desired learning experiences The curriculum, therefore, may


10 Implementation Curriculum Instruction Teacher Development And Assessment A Framework For K 12 Science Education Practices Crosscutting Concepts And Core Ideas The National Academies Press
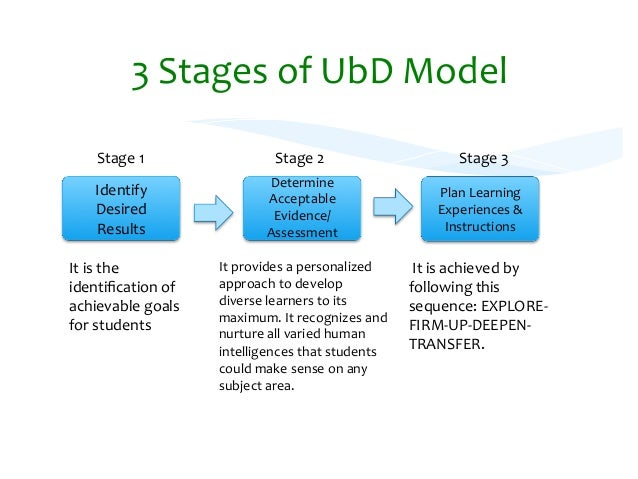


Curriculum Models Philippines Curriculum Models
What are the models of curriculum development?Recent DepEd Memoranda February 5, 21 DM 002, s 21 – Ulirang Guro 21 ng Komisyon ng Wikang Filipino;Tyler developed this educational model because he felt that educational programs lacked clearly defined goals and objectives for the purpose of measuring student achievement in the course Ralph Tyler interpreted that the vast majority of educational curriculum was defined by a sense of inflexibility and restriction, rather than goaloriented and directed learning activities



Content Based Foreign Language Teaching Curriculum And Pedagogy For D
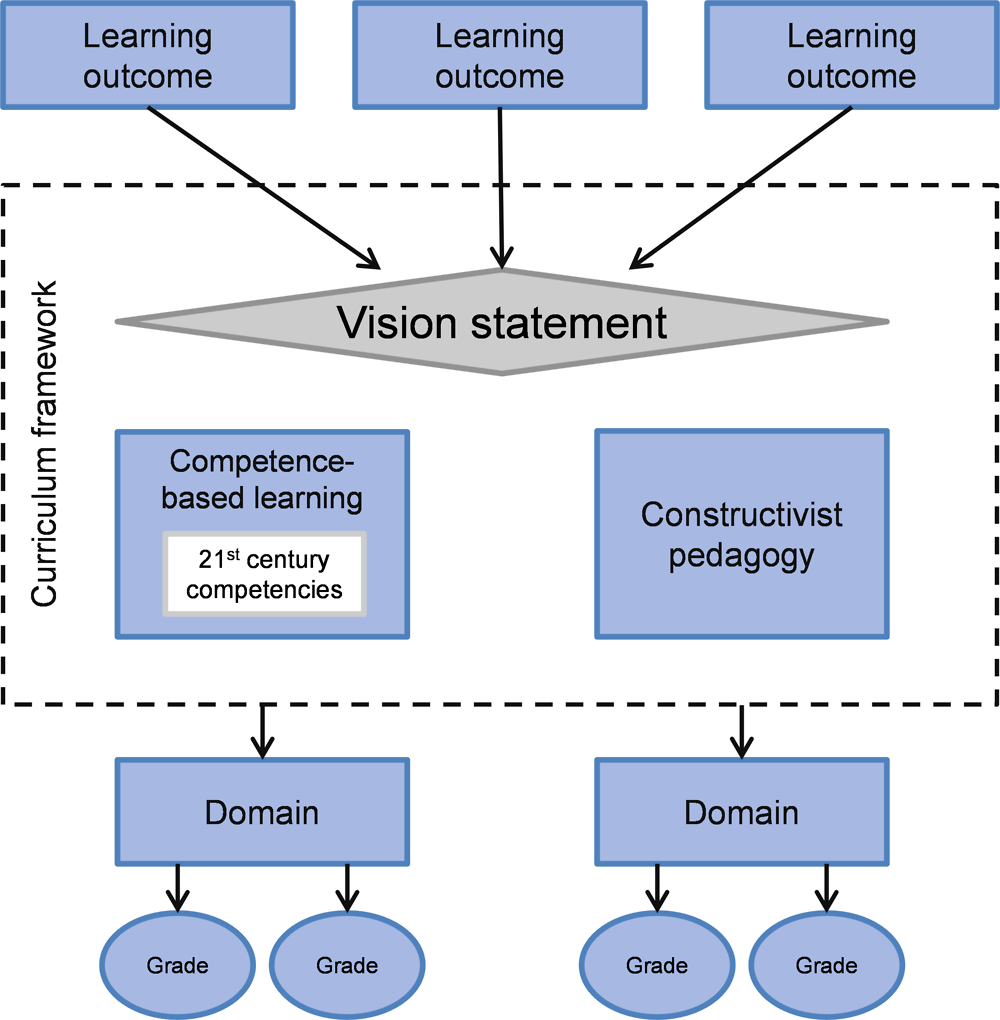


Promoting National Goals For Student Learning Oecd Reviews Of Evaluation And Assessment In Education Student Assessment In Turkey Oecd Ilibrary
23 Curriculum change and management in South African Schools before 1994 14 24 Curriculum change and management in South African Schools after 1994 16 25 Models of managing curriculum change 19 251 OvercomingResistance to Change Model (ORC) viiCurriculum models (Philippines' Curriculum Models) 1 Public School Curriculum Philippines' Public School Curriculum Model Adora A Barnachea CE 217 – Graduate Program, Miriam College Sept , 13 Ma • Education during pre‐Martial Law – The 2‐2 plan which provided common curriculum in the 1st and 2nd years, vocationalCurriculum planning Edit for timeliness • Review the maps for timely issues, breakthroughs, methods, materials, and new types of assessment • Be vigilant about technology Edit for Coherence • Scrutinize maps for a solid match between the choice of content, the featured skills and



Health Policy Development And Planning Bureau Department Of Health Philippines



Linear Model Of Curriculum She S Journal
Models of Curriculum Evaluation 1 Concept of Model 2 Need for Models 3 Models of Curriculum Evaluation 1 Tyler's Model 2 CIPP Model 3 Stake's Model 4 Roger's Model 5 Scriven's Model 6 Krikpatricks model 4 Criteria for judging evaluation studiesCurriculum Analysis Introduction Curriculum is the "All the learning which is planned and guided by the school, whether it is carried on in groups or individually, inside or outside of school" (Mccoy, 13) To develop or revise nursing curriculum is a difficult task and requires a thorough knowledge of the curriculum development process


Instructional Design Models And Theories Educational Technology



Learning Services Curriculum Development


Understanding Regionalisation In Philippine Higher Education Emerald Insight
/curriculum-design-definition-4154176_final-997bf6be4c1f488883765441c2181c23.png)


Curriculum Design Definition Purpose And Types


Full Article English Curriculum Reform In The Philippines Issues And Challenges From A 21st Century Learning Perspective



Competency Based Curriculum Importance Challenges Of Implementation



Curriculum Design And Models



Like The Layers Of An Onion Curricular Noticing As A Lens To Understand The Epistemological Features Of The Philippine K To 12 Secondary Mathematics Curriculum Materials Springerlink



Key Issues In Curriculum Assessment And Ict In Basic Education By Center For Integrative And Development Studies Publications Issuu


Curriculum Development Guide Population Education For Non Formal Education Programs Of Out Of School Rural Youth



Curriculum Management W Pop Quiz 07



Developing A Curriculum For The Transition Program Of Special Learners In The Philippines Semantic Scholar



6 Adult Learning Theories Put Theory Into Practice



Doc Historical Evolution Of Educational Goals And Objectives In The Philippines 1hr0ivc Takeshi Perez Academia Edu


Outcome Based Education In Accounting The Case Of An Accountancy Degree Program In Sri Lanka Emerald Insight



Instructional Design Wikipedia



Bringing Governance Back Into Education Reforms
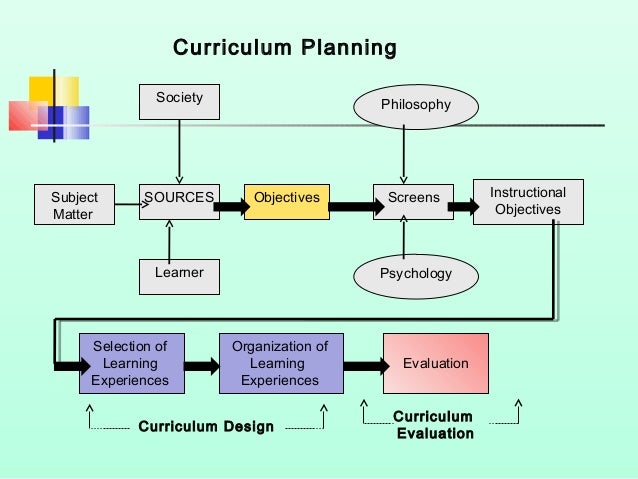


Curriculum Models And Types



Understanding By Design Center For Teaching Vanderbilt University



Amazon Com Curriculum Development The Philippine Experience Ebook Bago Adelaida Kindle Store



Curriculum Planning Process Development Educational Psychology Class Video Study Com



Curriculum Planning In The Philippines


Curriculum Development Guide Population Education For Non Formal Education Programs Of Out Of School Rural Youth
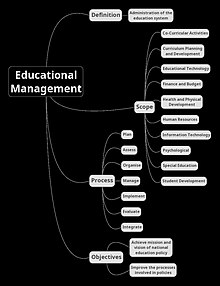


Educational Management Wikipedia



Modernising The Curriculum And Assessment Practices Education In Saudi Arabia Oecd Ilibrary


Types Of Curriculum Models Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



The Philippine Innovation Act The National Economic And Development Authority



Curriculum Evaluation Goal Based Vs Goal Free The Elastic Scholastic



Competency Based Curriculum Importance Challenges Of Implementation



Writing Curriculum Aims Goals Objectives


Ralph W Tyler 1902 1994 Curriculum Development Model Dr V K Maheshwari Ph D
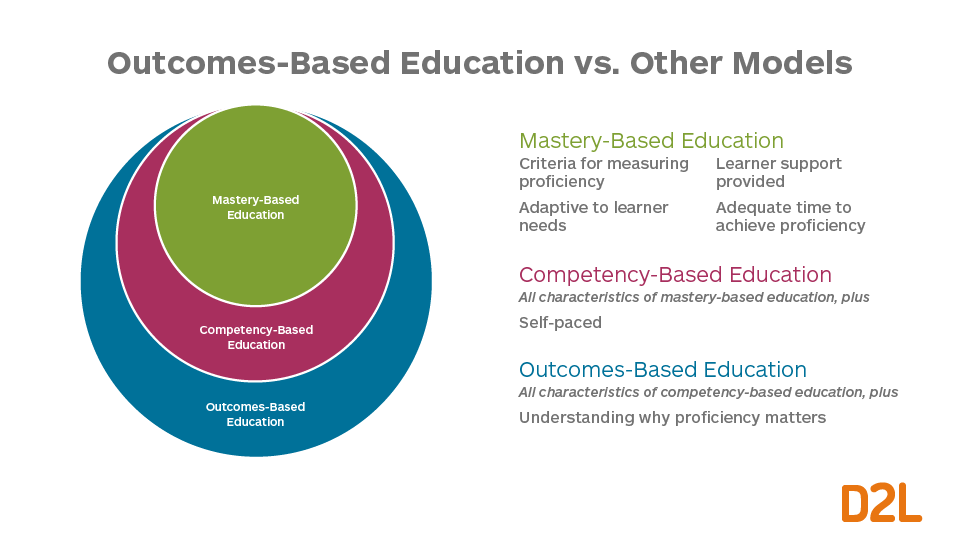


Unboxing Outcomes Based Education What Is Obe D2l



Routledge International Handbook Of Medical Education



Pdf Language Curriculum Development An Overview



Curriculum Planning In The Philippines


Full Article Community Development Approaches And Methods Implications For Community Development Practice And Research
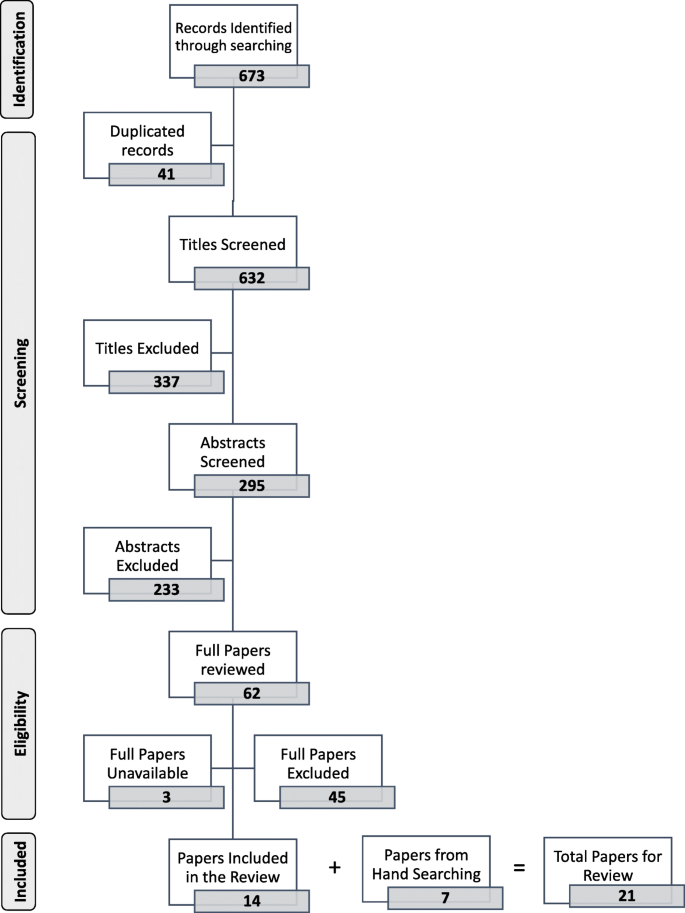


Curriculum Management Monitoring In Undergraduate Medical Education A Systematized Review Springerlink



Health Policy Development And Planning Bureau Department Of Health Philippines


Obe Principles And Process Cei Center For Education Innovation



Curriculum My Inner Classroom



Curriculum Planning In The Philippines



Deped Philippines Deped Teaches Episode 1 Overcoming Challenges In Curriculum Facebook
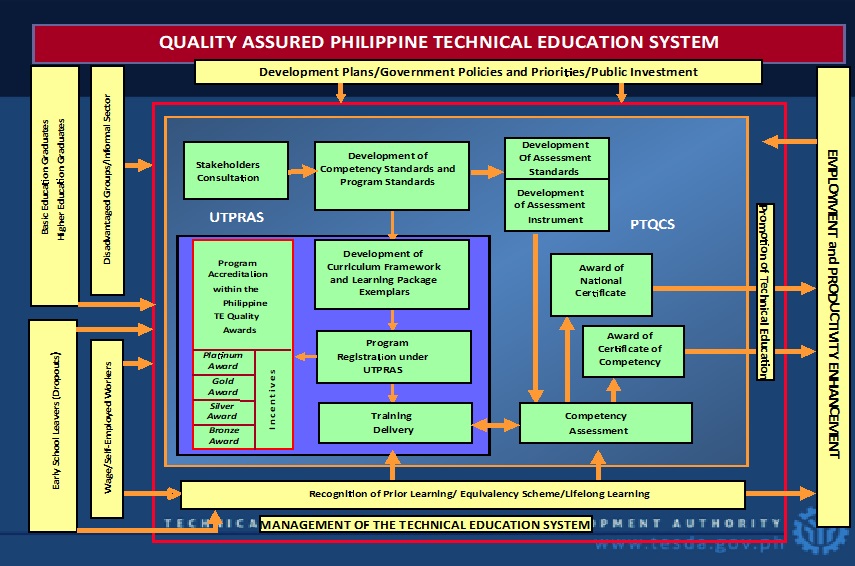


Details Philippine Qualifications Framework



Laguna State Polytechnic University Curriculum Design


Promoting National Goals For Student Learning Oecd Reviews Of Evaluation And Assessment In Education Student Assessment In Turkey Oecd Ilibrary



Chapter 5 Curriculum Development And Planning Curriculum Goal



Curriculum Development Using Effective Goals And Objectives



Types Of Curriculum Models Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Curriculum Development Finals Education Quiz Quizizz



Linear Model Of Curriculum She S Journal



Education For Social Change From Theory To Practice
/curriculum-design-definition-4154176_final-997bf6be4c1f488883765441c2181c23.png)


Curriculum Design Definition Purpose And Types



Writing Curriculum Aims Goals Objectives



Projects Organized By Un Sustainable Development Goal Asia Society



Curriculum Planning In The Philippines



Quiz 1 Curriculum Planning And Development Quiz Quizizz



Curriculum Planning In The Philippines



Pdf Outcomes Based Approach To Pharmacy Curriculum Review And Redevelopment



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿